
What is Emotional Intelligence?
![]() The term “emotional intelligence” was first coined in 1990 by Professors Peter Salovey and John D. Mayer. They conducted significant research and created numerous articles on Emotional Intelligence. (EI)
The term “emotional intelligence” was first coined in 1990 by Professors Peter Salovey and John D. Mayer. They conducted significant research and created numerous articles on Emotional Intelligence. (EI)
During the 1990’s , Daniel Goleman, an American psychologist, came across Salovey and Mayer’s work, he explored their research and developed a framework of five elements that define emotional intelligence and this eventually led to his book "Emotional Intelligence - Why It Can Matter More Than IQ" being published in 1995.
In his book, Goleman promoted the concept that Emotional Intelligence was more important than natural intelligence (IQ) in determining success in life and Goleman argued that it was not cognitive intelligence that guaranteed business success but actually emotional intelligence estimating that up to 80% of success is down to EI – your emotional competence – leaving just 20% attributable to IQ or knowledge and skills. He describes EI as the ability to identify, assess, and control one’s own emotions, the emotions of others, and that of groups. Goleman outlines the collection of psychological traits and skills which he says are key to success and explains how they determine people’s success at work, relationships, and their overall well-being.
He described emotionally intelligent people as those with four characteristics:
- They were good at understanding their own emotions (self-awareness)
- They were good at managing their emotions (self-management)
- They were empathetic to the emotional drives of other people (social awareness)
- They were good at handling other people’s emotions (social skills)
Goleman’s’ 5 areas are
Self-Awareness – People with high emotional intelligence are usually very self-aware . They understand their emotions, and because of this, they don't let their feelings rule them. They're confident – because they trust their intuition and don't let their emotions get out of control. They're also willing to take an honest look at themselves. They know their strengths and weaknesses, and they work on these areas so they can perform better. Many people believe that this self-awareness is the most important part of emotional intelligence.
Self-Regulation – This is the ability to control emotions and impulses. People who self-regulate typically don't allow themselves to become too angry or jealous, and they don't make impulsive, careless decisions. They think before they act. Characteristics of self-regulation are thoughtfulness, comfort with change, integrity, and the ability to say no.
Motivation – People with a high degree of emotional intelligence are usually motivated. They're willing to defer immediate results for long-term success. They're highly productive, love a challenge, and are very effective in whatever they do.
Empathy – This is perhaps the second-most important element of emotional intelligence. Empathy is the ability to identify with and understand the wants, needs, and viewpoints of those around you. People with empathy are good at recognizing the feelings of others, even when those feelings may not be obvious. As a result, empathetic people are usually excellent at managing relationships , listening , and relating to others. They avoid stereotyping and judging too quickly, and they live their lives in a very open, honest way.
Social Skills – It's usually easy to talk to and like people with good social skills, another sign of high emotional intelligence. Those with strong social skills are typically team players. Rather than focus on their own success first, they help others develop and shine. They can manage disputes, are excellent communicators, and are masters at building and maintaining relationships.
Benefits of a high EI
A high EQ helps individuals to communicate better, reduce their anxiety and stress, defuse conflicts, improve relationships, empathize with others, and effectively overcome life’s challenges.
Our emotional intelligence affects the quality of our lives because it influences our behaviour and relationships. It raises our self-awareness and it enables us to live our lives with intention, purpose, and autonomy. EI can profoundly affect our choices by creating options we may not have otherwise imagined or considered to be possibilities.
- For the individual
The benefits are increased self-confidence, an increased willingness to speak their mind, an increased willingness to fight for what they deem important and a greater resilience to the challenges and changes they face in both their organizational and personal lives.
- For organisations
The benefits to organisations of having emotionally intelligent people are numerous. Emotionally intelligent people are more confident, more motivated, more committed to the purpose of their organisation and better able to apply their unique skills to the tasks at hand. In addition to being more willing to share their creative ideas, emotionally intelligent people build better relationships both with colleagues and clients.
Can you improve your EQ?
Yes.!
Goleman believes that emotional competencies are not innate talents, but rather learned capabilities that can be learned, improved and worked on to achieve outstanding performance.
It’s the foundation for dealing with impulses, dealing with stress, and actually responding and reacting in a way that you would want.
So, developing Emotional intelligence is the key to improving personal effectiveness.
As a leader or manager, developing your EQ will better improve your chance of building successful relationships with peers and team members and leading your teams to achieve business results.
However, if you have to want to get better at it, you have to be motivated to do it.
So, where do you start?
You can measure your levels of Emotional intelligence using an assessment.
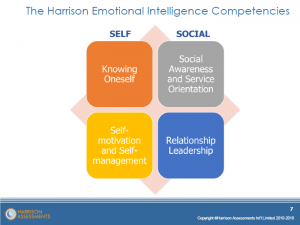
Harrison Assessments have simplified Goleman’s 5 elements and produced 4 behavioural competencies which enable direct objective measurement of Emotional Intelligence
and provides a detailed insight into the four areas of emotional intelligences including:
- Knowing Oneself,
- Relationship Leadership,
- Self-Motivation & Self-Management,
- Social Awareness & Service Orientation
highlighting Essential Traits, Desirable Traits and Traits to Avoid in each.


Want to explore your Emotional intelligence?
Here are several options for you
Option 1
Download our FREE 19 page Harrison assessment EI Sample Report - FREE - Click here
see a sample Harrison EI report. get a feel of what it looks like and decide if it’s something you would like to do for yourself.
Option 2
Find out about your Emotional Intelligence with a personalised one page overview of the 4 high level areas of emotional intelligence - FREE
Click here fill out the contact form to complete a 20 minute online SmartQuestionnaire™ and receive a 1 page high level EI report
scoring the 4 key areas of
Knowing oneself
Relationship Leadership
Self -motivation and Self -Management
Social Awareness and Service Orientation
Option 3
A full personalised 19 page EI report – £72 + vat -
email Christine@utransition.co.uk to complete a 20 minute online SmartQuestionnaire™
receive a full EI report (A one page overview and 4 detailed Individual Competency Reports providing a comprehensive understanding of an individual’s attitudes and behaviours that impact his/her level of the competency against each of the four areas. _
Option 4
A full personalised EI report and online Emotional Intelligence training course - £105+vat
email Christine@utransition.co.uk to complete a 20 minute online SmartQuestionnaire™ and receive the online course
Complete a 20 minute online SmartQuestionnaire™ and receive a full personalised 19 page report (overview and Individual Competency Reports providing a comprehensive understanding of an indiividual’s attitudes and behaviours that impact his/her level of the competency against each of the four areas.
Online course This course will introduce the concept of emotional intelligence and look at how you can use it in effective and meaningful ways. It will examine the difference between emotional intelligence and IQ and dispel some of the myths surrounding emotional intelligence. It contains a section on the advantages and disadvantages of using emotional intelligence and considers the biological purpose for emotions and how best to manage them.
it will highlight the role played by emotions in the workplace and provide practical advice including tips for using emotional intelligence to deal effectively with emotions in situations that can arise in the workplace.
Target Audience
This course is aimed at supervisors and managers that want to develop more effective relationships with members of their teams. The course can be a great starting point for people new to their leadership role as well as more established managers that want to enhance their skills. This acts as a great introduction to the subject and covers the key concepts and theories relating to emotional intelligence.
2 CPD points
Modules:
What is Emotional Intelligence?
Understanding and recognising emotions
Emotional Intelligence at work
Tips for dealing with emotions at work
Duration: 50 minutes
